Autologous bone graft is used in various situations in orthopedics, traumatology and mainly in reconstructions of orthopedic oncological surgeries.
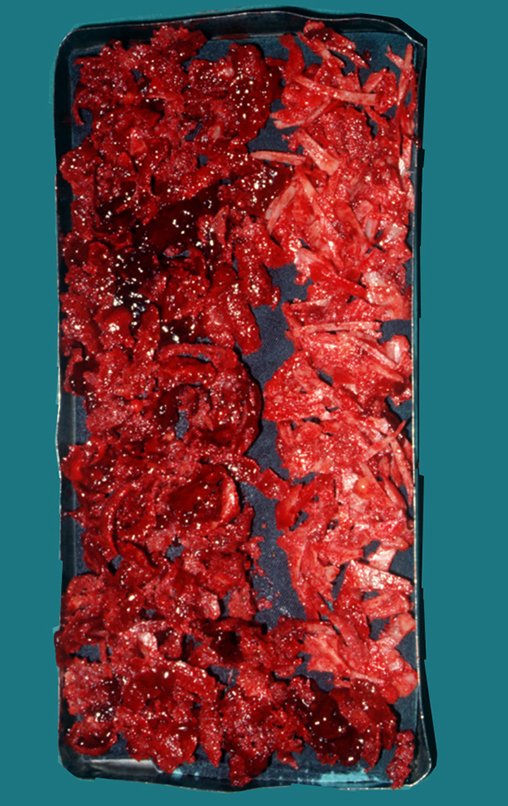
In bone defects, it is certainly what promotes the best and fastest bone consolidation, has the best integration and fastest remodeling.
Secondly, we can resort to homologous bone graft, bone from a tissue bank, obtained from a cadaver, which has the disadvantage of antigenicity, has a higher rate of infection, takes longer to incorporate and structural fragility can occur in the integration process. Lastly, we can mention artificial freeze-dried products, which aim to be osteoinductive.
Our objective is to publicize the technique we use to obtain the greatest amount of bone graft with the lowest morbidity.
We believe that, whenever it is possible to use the autologous graft, we will be providing the alternative that allows the best result.
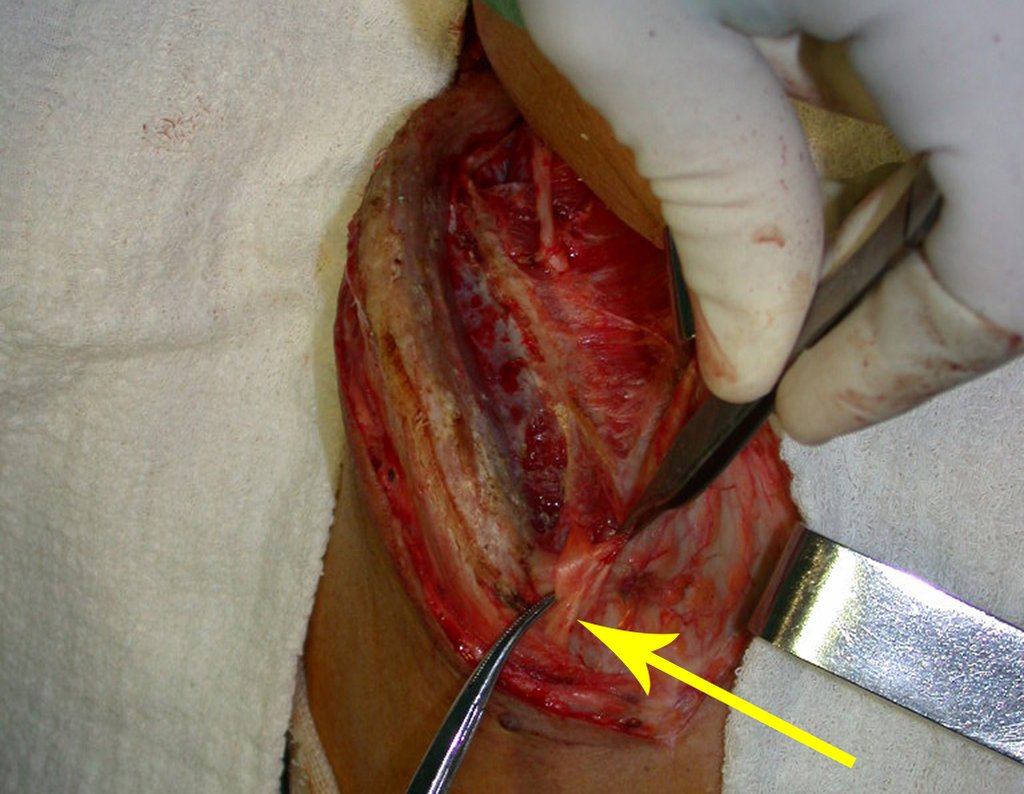
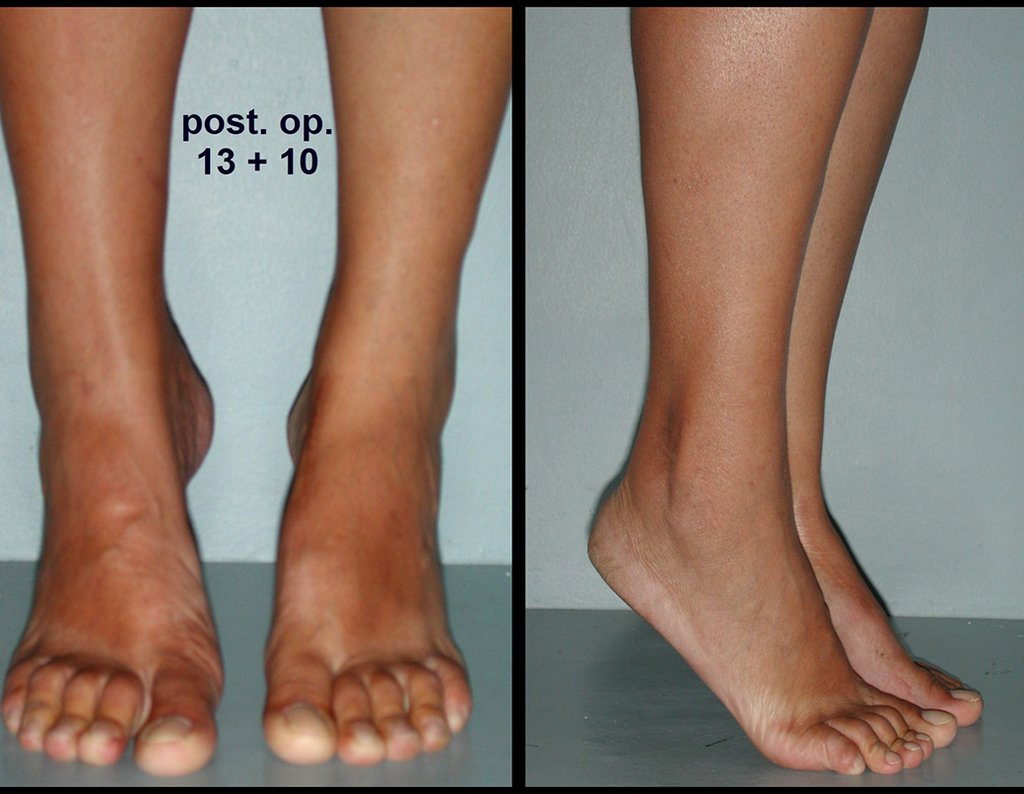
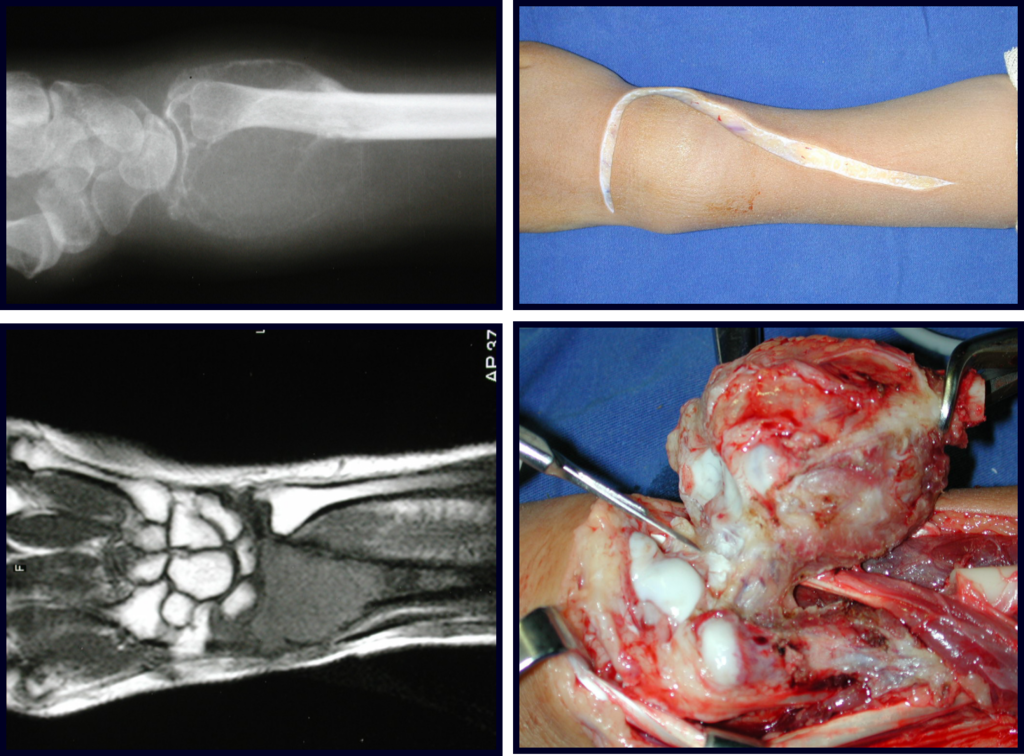
When we need a small amount of graft, we don’t question its indication too much. As an example, in the case of the need to resect the proximal 3/4 of the radius, due to a tumor lesion, which we intend to resolve by performing a distal radio-ulnar “synostosis”, figures 1 to 4.
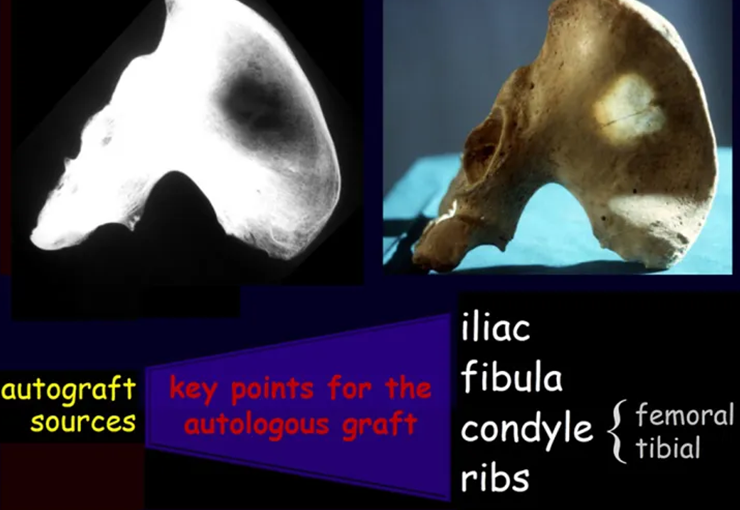
Autologous bone graft – Obtaining techniques
Há três décadas atuamos no Instituto do Câncer Dr. Arnaldo Vieira de Carvalho, o primeiro Hospital do Câncer do Brasil, completando 95 anos neste ano de 2016, figura 5 e 6.
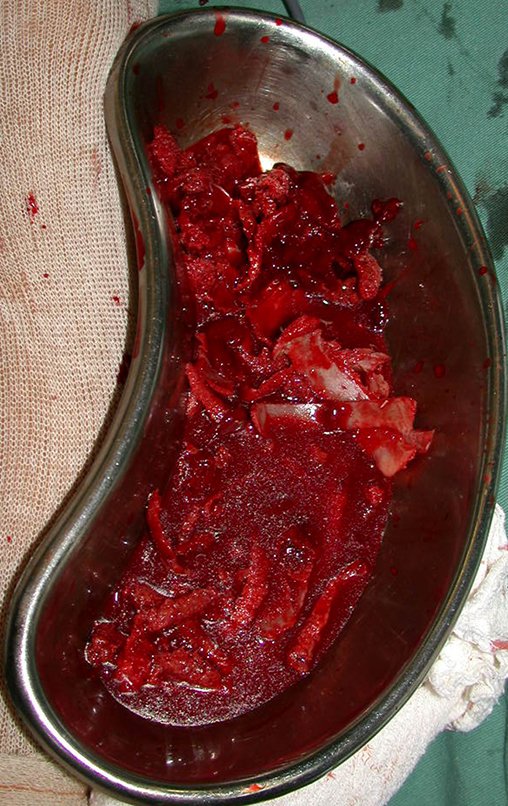
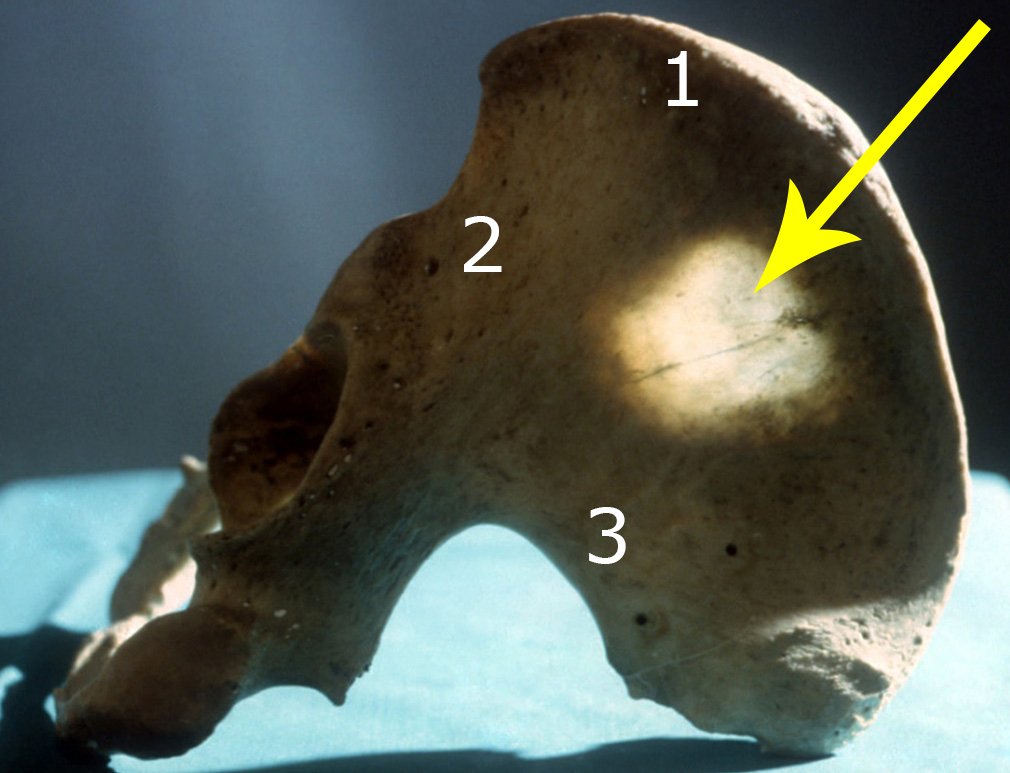
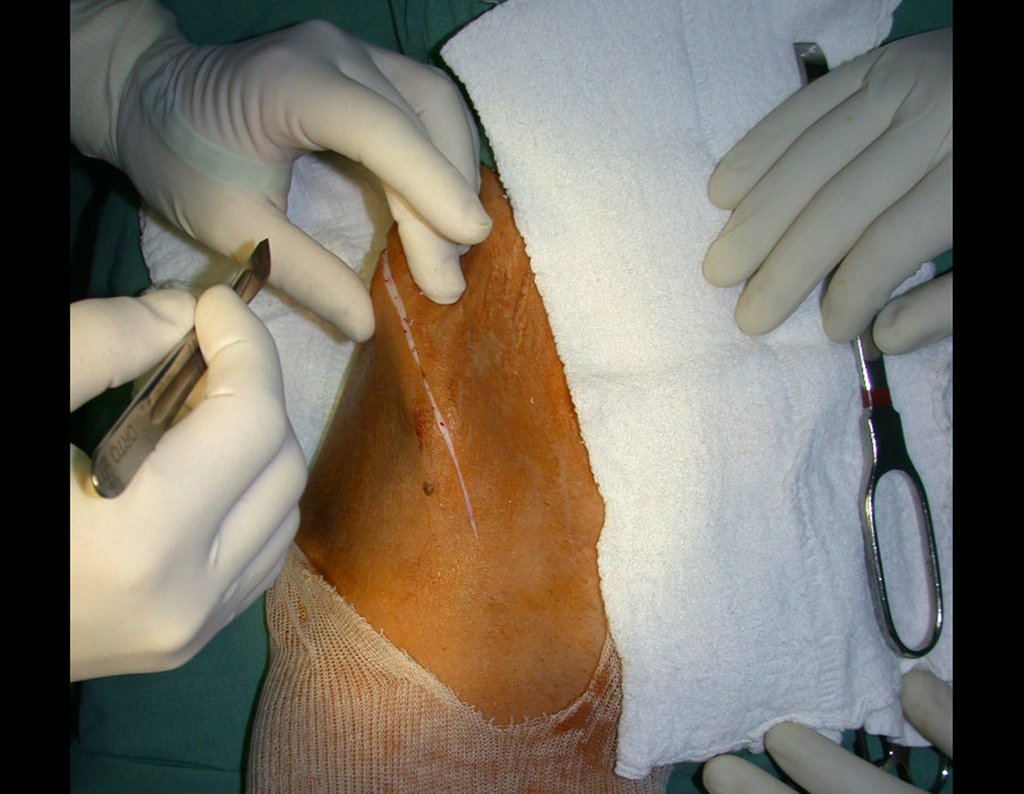
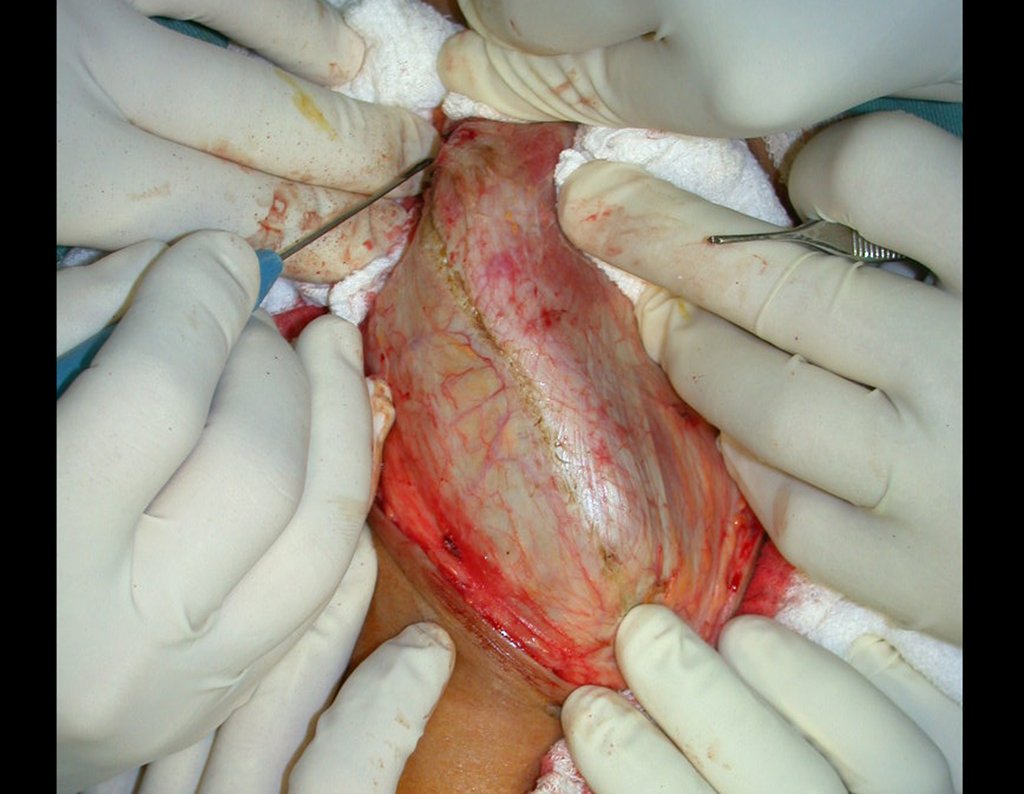
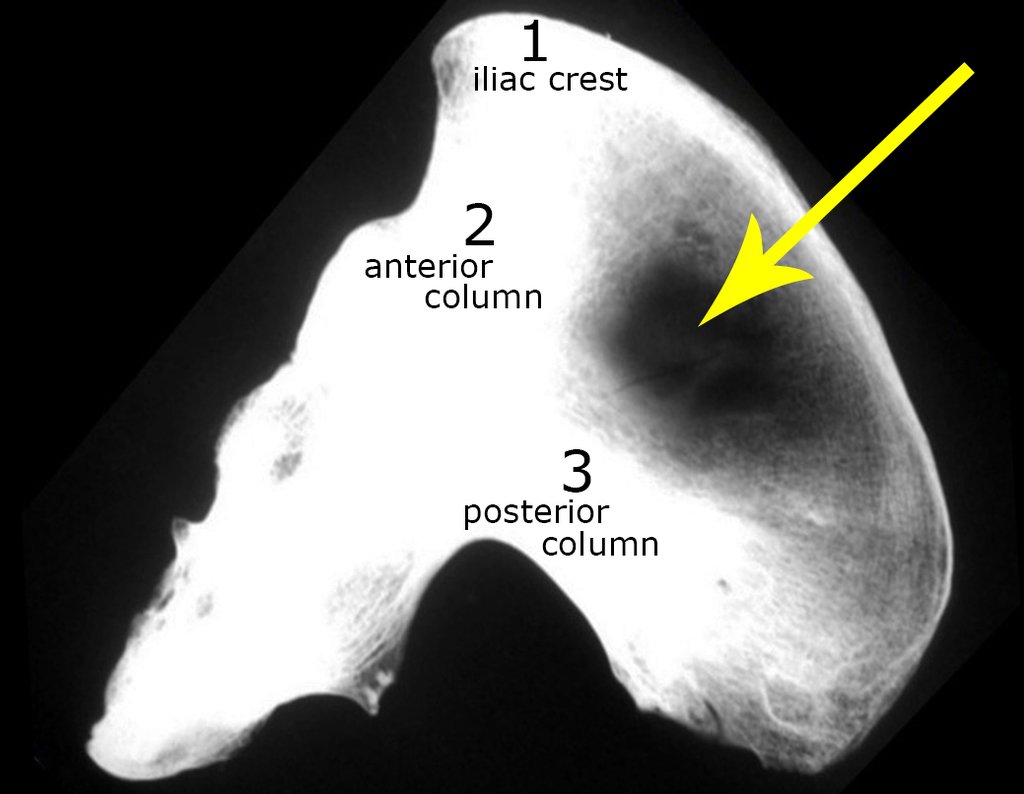
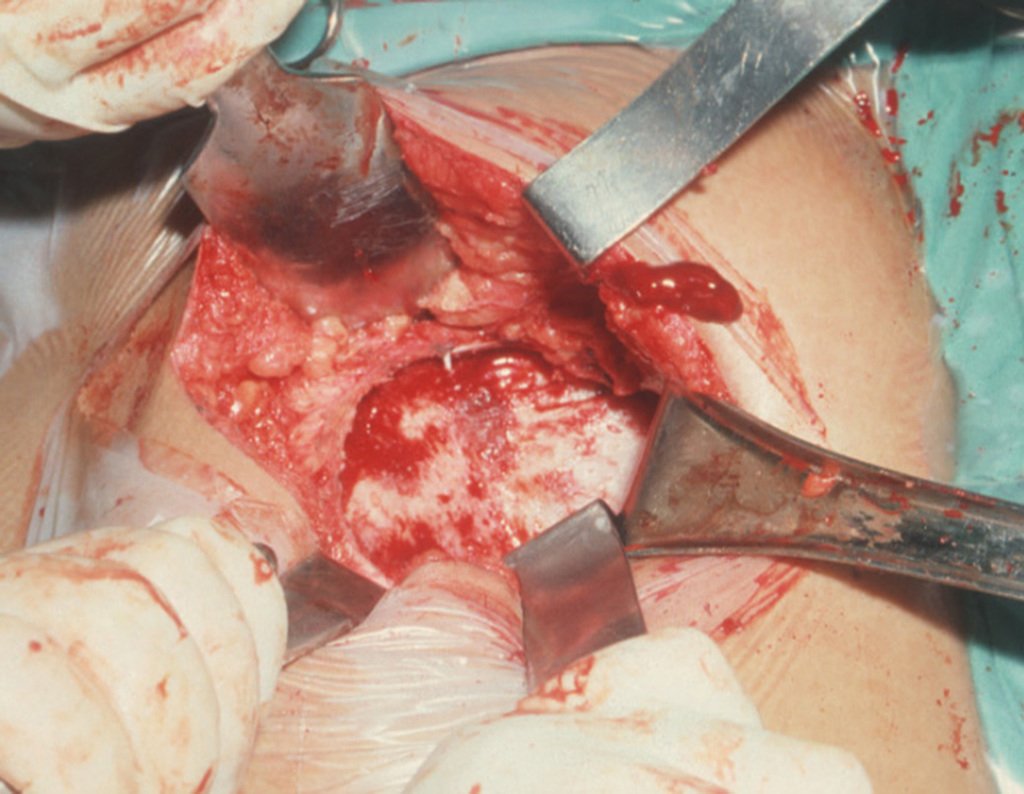
After removing the entire inner cortex, we store the graft in a vat, soaked by the collected clot, thus preserving the totipotent cells, which will also be placed in the bone defect. Next, with a sharp chisel and WITHOUT using a hammer, we proceed with the removal of the spongy iliac bone, figures 20 to 23.
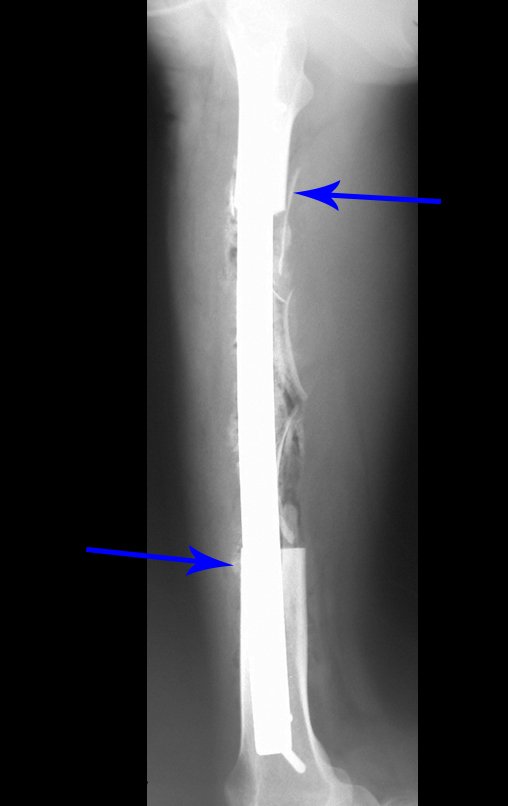
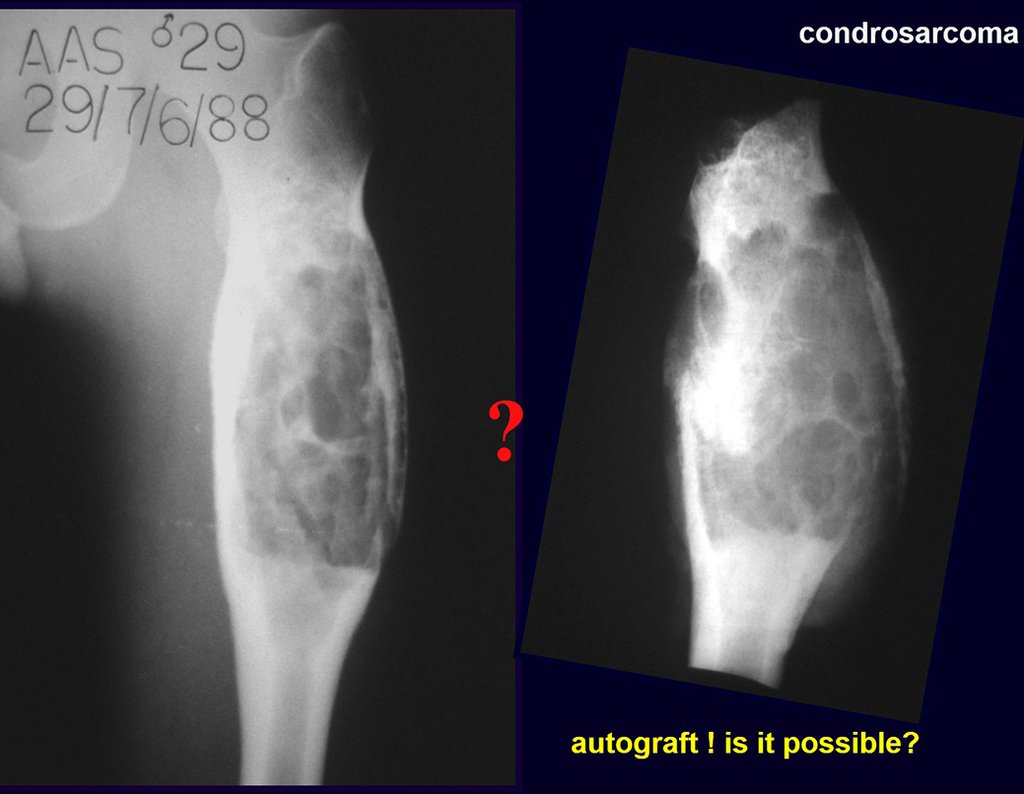
It is important to remember the concept of repairing bone defects with bone grafts: IN A BIOLOGICAL RECONSTRUCTION, EVERY BONE GRAFT PLACED TO FILL CAVITIES OR SEGMENTAL FAULTS GOES THROUGH A REABORTION PHASE TO BE LATER REINTEGRATED , REPAIRING THE BONE LOSS. The graft must be intertwined and go beyond the level of the osteotomy, avoiding pseudarthrosis, as exemplified by this case of chondrosarcoma in figures 36 to 38, blue arrows.

This case can be seen in full by accessing the link: http://bit.ly/sarcoma-de-Ewing
The fibula can also be used vascularized in reconstructions, including with the growth plate to replace the one that will be resected due to the tumor. It is a fibula autotransplantation with the physeal plate, performing osteosynthesis with the extensible internal fixation device, figures 63 and 64.
In the reconstruction of small segments, such as in reconstruction of the radius, due to trauma or tumors, we can use the free fibula with good results, figures 65 and 66.
This case can be seen in full by accessing the link: http://bit.ly/tgc_radio
Author: Prof. Dr. Pedro Péricles Ribeiro Baptista
Orthopedic Oncosurgery at the Dr. Arnaldo Vieira de Carvalho Cancer Institute
Office : Rua General Jardim, 846 – Cj 41 – Cep: 01223-010 Higienópolis São Paulo – SP
Phone: +55 11 3231-4638 Cell:+55 11 99863-5577 Email: drpprb@gmail.com